How to update a record using JDBC PreparedStatement
jdbc
PreparedStatement
update
update record with jdbc

In this tutorial will try to update records from a database table using JDBC PreparedStatement. For more resources about JDBC please follow the links from references section.
Example
To be easier for this tutorial I will copy all necessary code from the tutorials listed on reference section.
package com.admfactory.db;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBCUpdateRecord {
private static Connection connect() {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/admfactory.com", "root", "");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Failed to connect to DB.");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
private static void updateData(long id, String name, String email, String password, String type, Date dob) throws Exception {
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
String query = "UPDATE `user` SET `name`= ?, `email`= ?, `password`= ?, `type`=?,`dob`=? WHERE `id`=?;";
Connection connection = connect();
statement = connection.prepareStatement(query);
statement.setString(1, name);
statement.setString(2, email);
statement.setString(3, password);
statement.setString(4, type);
statement.setDate(5, dob);
statement.setLong(6, id);
int r = statement.executeUpdate();
/** Check if the user was successfully updated. */
if (r > 0) {
System.out.println("User [" + name + ", " + email + "] was successfully updated.");
} else {
System.out.println("Failed to update user id " + id);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
System.out.println("Update one record.");
/** Get the connection. */
Connection connection = connect();
if (connection != null) {
/** update some data. */
updateData(1, "John22 Doe22", "john22@gmail.com", "pass22", "ADMIN", new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
System.out.println("Record updated successfully!");
/** Close the connection. */
connection.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Something went wrong.");
}
}
}
Note that the index for the statement object starts from 1.
Output
Update one record.
User [John22 Doe22, john22@gmail.com] was successfully updated.
Record updated successfully!
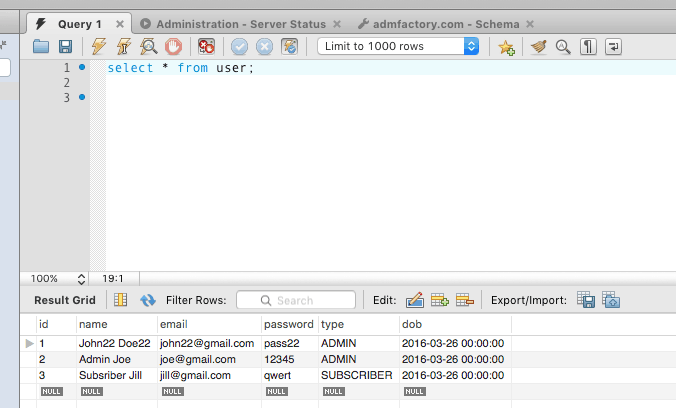
Conclusion
To verify that the data was modified you can use any database editor like MySQL Workbench.